
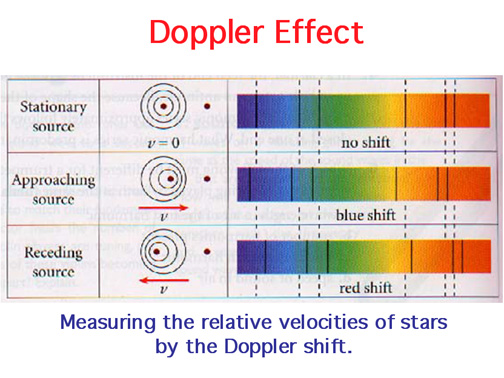
Red shift is the movement of spectral lines which is towards the longer wavelengths which is the red end of the spectrum in radiation from the distant galaxies and the celestial objects.Ī red shift is any increase in wavelength with the corresponding decrease in the frequency of an electromagnetic wave. Doppler’s effect can be defined as the change in the frequency of the wave with respect to an observer which is moving relative to the wave source. Doppler shift is also known as Doppler’s effect. It is used to refer to any shift towards higher frequencies, including types of electromagnetic radiation where the frequencies do not correspond to any visible colour, and more generally to other types of waves (for example, gravitational waves).Hint :The redshift and blueshift is observed in the doppler shift. In the light of that, the term 'blueshift' has acquired a more general meaning. If the frequency of a light wave is shifted towards higher frequencies (for instance by the doppler shift), that corresponds to a colour shift towards the blue-violet end of the spectrum, and is hence called a blueshift. For the highest possible frequencies of visible light, the colour is blue-violet. blueshift The frequency of a simple light wave is directly related to its colour (cf. In the context of quantum theory, it turns out that electromagnetic radiation consists of tiny energy packets, called light particles or photons. electromagnetic radiation Electromagnetic influences (in the language of physics: electric and magnetic field) which, even with no electric charges present, are locked in a state of mutual excitation so that they form a wave that propagates through space.Īs this wave transports energy, it is, by the usual physics definition, a form of radiation, called electromagnetic radiation.ĭepending on frequency, there are special names for different types of electromagnetic radiation going from lower to higher frequencies: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. Ten maxima going by per second correspond to a frequency of 10 Hz. (The unit Hertz, abbreviated as Hz, is defined as 1 Hz = 1/second.)įor a simple wave, the frequency is given by the number of maxima going by a stationary observer in a second. Measure for the rapidity of an oscillation, defined as the inverse of the period of oscillation: A process that, in oscillating, repeats itself after 0.1 seconds has the frequency 1/(0.1 seconds)= 10 Hz.
Also, there are a number of interesting effects in general relativity which are associated with the propagation of light, namely deflection, the Shapiro effect and the gravitational redshift. First of all, the speed of light plays a central role in both special and general relativity. In the context of relativistic physics, light is of great interest, and for a number of reasons.

Within classical physics, the properties of light are governed by Maxwell's equations in quantum physics, it turns out that light is a stream of energy packets called light quanta or photons. For instance, astronomers might talk about "infrared light" or "gamma light" in this context, light in the stricter sense is referred to as "visible light". In relativity theory and in astronomy, the word is often used in a more general sense, encompassing all kinds of electromagnetic radiation. light Light in the strict sense of the word is electromagnetic radiation the human eye can detect, with wave-lengths between 400 and 700 nano metres. In a more restricted sense, the word is often used synonymously with electromagnetic radiation. In a general sense: Collective name for all phenomena in which energy is transported through space in the form of waves or particles. The spectrum lists the composition of this mix: For every frequency, it states the amount of radiation energy contributed by waves of that particular frequency. spectrum The electromagnetic radiation reaching us from an astronomical object or other source is a mix of electromagnetic waves with a great variety of frequencies.

Simple examples are water-waves - wave crests and troughs travelling over a water surface, and a Mexican wave in a football stadium, with fans alternately standing up and sitting down - the pattern moves throught the stadium, not the fans themselves.Īn especially simple form for a wave is a sinus wave, a regular pattern of wave crests and troughs. In a general sense: any travelling pattern, whether or not it involves matter being transported as well.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
